PolyMem for Radiotherapy
PolyMem therapy is a soft, absorbent, conformable dressing with moisturising and wound cleansing ingredients which is indicated for radiotherapy-induced skin damage.
Designed to facilitate healing, relieve pain and reduce inflammation, PolyMem therapy is a multifunctional polymeric membrane dressing.
Product Benefits
PolyMem dressings are a hydrophilic polyurethane matrix dressing with a mild, non-toxic wound cleanser, a soothing moisturiser, a superabsorbent and a semi-permeable film backing*.
When PolyMem is applied to the wound, the dressing components work individually and synergistically to support wound healing and pain relief¹.
For radiotherapy patients, PolyMem therapy has proved to:
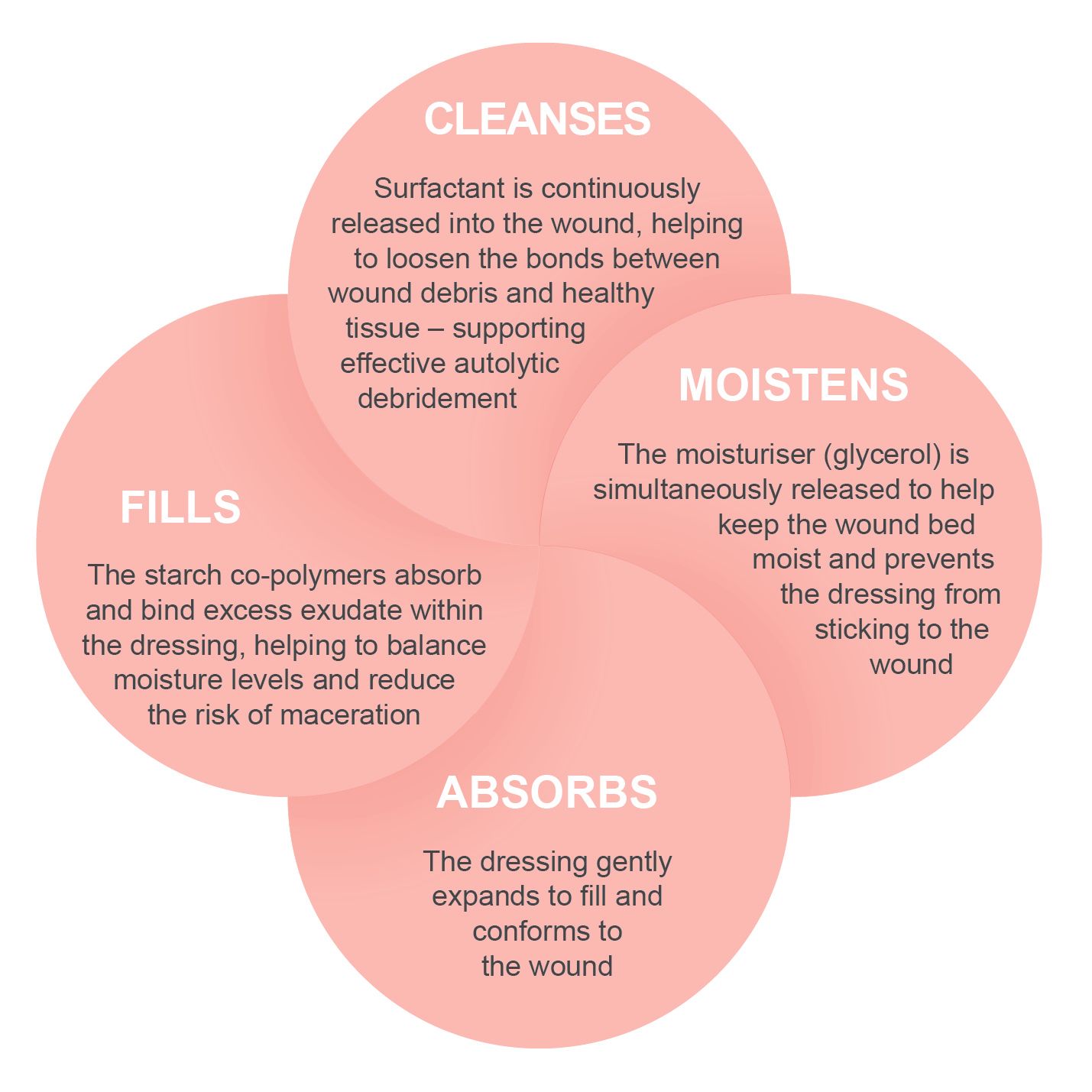
How the PolyMem formulation works:
All PolyMem dressings effectively cleanse, fill, absorb and moisten wounds throughout the healing continuum. The diagram below explains how each of these elements work.
1. Denyer J, Agathangelou C, White R, Ousey K, HariKrishna R et al (2015) PolyMem Made Easy. Wounds International. Available at https://www.woundsinternational.com/resources/details/polymem-dressings-made-easy.
2. Beitz AJ, Newman A, Kahn AR et al (2004) A polymeric membrane dressing with antinociceptive properties: analysis with a rodent model of stab wound secondary hyperalgesia. J Pain 5(1): 38–47.
3. Cutting KF, Vowden P, and Wiegand C (2015) Wound inflammation and the role of a multifunctional polymeric dressing. Wounds International 6(2): 41–6.
4. Benskin LL (2016) Polymeric membrane dressings for topical wound management of patients with infected wounds in a challenging environment: A protocol with 3 case examples. Ostomy Wound Manage 62(5): 42–50.
5. Kahn AR (2000) A superficial cutaneous dressing inhibits inflammation and swelling in deep tissues. Pain Med 1(2): 187.
*Excluding Wound In Cavity (WIC) dressings.